
PNU 리서치
- 메인으로 이동
- 연구/산학
- PNU 리서치

생명과학과 윤부현 교수 연구팀이 암세포 중에서도 치료가 잘되지 않고 재발과 전이를 유도하는 ‘암 줄기세포(Cancer Stem Cells, CSC)’의 복잡한 메커니즘을 규명해, 표적 치료를 통한 난치암 극복 가능성을 열었다.
이번 연구는 암의 재발과 전이를 유발하는 암 줄기세포의 이질성과 대사 유연성을 분석함으로써, 기존 치료의 한계를 극복할 수 있는 새로운 치료 방향을 설정했다.
연구팀은 암 줄기세포가 보유한 대사 및 표현형의 유연성이 암 치료 저항성의 중요한 원인이라는 최근 연구들을 종합해 고찰하고, 이를 바탕으로 효과적인 치료 접근법의 방향을 잡았다. 특히, 단일세포 오믹스(omics·體學)와 공간 전사체 분석 등 최신 기술을 통해 알려진 암 줄기세포의 이질성과 대사 적응 메커니즘에 주목하며, 이를 활용한 이중 대사 억제 및 면역 기반 치료 전략의 가능성을 소개했다.
‘암 줄기세포’는 암세포 중에서도 치료에 강한 저항성을 보이며, 종양의 재발과 전이를 유도하는 핵심 집단으로 주목받고 있다.
대사 가소성(plasticity) 덕분에 암 줄기세포는 당을 분해하는 작용과 산화적 인산화, 그리고 글루타민과 지방산 같은 대체 연료원 사이를 전환해 다양한 환경 조건에서 생존할 수 있다. 또한, 기질 세포, 면역 구성 요소, 혈관 내피 세포와의 상호작용은 대사 공생을 촉진해 암 줄기세포의 생존과 약물 내성을 더욱 촉진한다.
기존 치료법을 회피하고 대사 스트레스에 적응하며 종양 미세환경과 상호작용하는 이러한 특성은, 암 줄기세포를 혁신적인 치료 전략의 중요한 표적이 되게 한다. 하지만 이들의 특성을 정밀하게 파악하고 표적한 연구는 지금까지는 초기 단계에 머물러 있었다.
연구팀은 이번 리뷰에서 암 줄기세포(CSC)의 치료 저항성과 관련된 최신 연구 동향을 분석·정리하고, 3D 오가노이드 모델*, CRISPR-Cas9(유전자가위) 기반 기능 분석, AI(인공지능) 융합 분석 기법 등의 응용 사례를 종합해 향후 CSC 정밀 타깃 치료 개발의 전망을 조망했다.
* 3D 오가노이드 모델: 줄기세포나 조직세포를 3차원적으로 배양해 실제 인체 기관과 유사한 구조와 기능을 재현한 실험 모델.
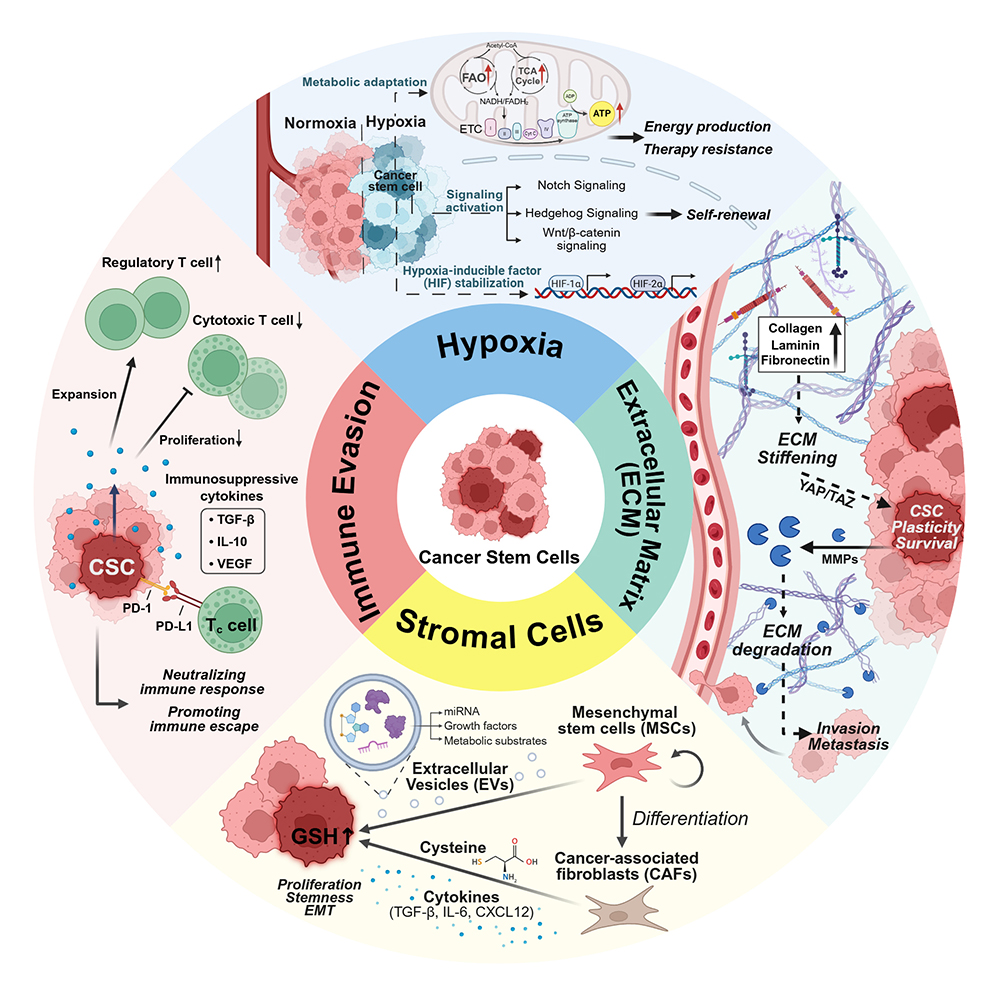
【암 줄기세포(CSC)의 생존과 악성화를 돕는 주변 환경 요인 분석】
연구책임자인 윤부현 교수는 “암 줄기세포는 기존 치료로 제거되지 않고 남아있다가 암을 재발시키는 주범으로, 이들의 대사적 생존 전략을 정밀 타격하는 것이 궁극적인 치료 혁신의 핵심”이라며 “이번 연구는 다양한 암에 적용 가능한 맞춤형 치료의 단초를 제공한 의미 있는 성과”라고 말했다.
해당 연구 결과는 생화학·분자생물학 분야 세계 최고 권위의 학술지인 『Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy』 8월 5일자에 게재됐다.
- 논문 제목: Cancer stem cells: landscape, challenges and emerging therapeutic innovations(암 줄기세포: 연구 현황, 도전 과제 및 신흥 치료 혁신)
- 논문 링크: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41392-025-02360-2
이번 연구는 생명시스템학과 이학수 박사와 김병수 박사과정생, 박준형 박사과정생이 제1저자, 세종대 윤혜숙 교수가 공동저자로 참여했으며, 생명과학과 윤부현 교수가 교신저자로 연구를 이끌었다. 한국연구재단 및 미래지구연구소 지원으로 수행됐다.
* 상단 연구진 사진: 왼쪽부터 윤부현 교수, 이학수 박사, 김병수 박사과정생, 박준형 박사과정생.
[Abstract]
Cancer stem cells (CSCs) represent a highly plastic and therapy-resistant cell subpopulation within tumors that drive tumor initiation, progression, metastasis, and relapse. Their ability to evade conventional treatments, adapt to metabolic stress, and interact with the tumor microenvironment makes them a critical target for innovative therapeutic strategies. Recent advances in single-cell sequencing, spatial transcriptomics, and multi-omics integration have significantly improved our understanding of CSC heterogeneity and metabolic adaptability. Metabolic plasticity allows CSCs to switch between glycolysis, oxidative phosphorylation, and alternative fuel sources such as glutamine and fatty acids, enabling them to survive under diverse environmental conditions. Moreover, interactions with stromal cells, immune components, and vascular endothelial cells facilitate metabolic symbiosis, further promoting CSC survival and drug resistance. Despite substantial progress, major hurdles remain, including the lack of universally reliable CSC biomarkers and the challenge of targeting CSCs without affecting normal stem cells. The development of 3D organoid models, CRISPR-based functional screens, and AI-driven multi-omics analysis is paving the way for precision-targeted CSC therapies. Emerging strategies such as dual metabolic inhibition, synthetic biology-based interventions, and immune-based approaches hold promise for overcoming CSC-mediated therapy resistance. Moving forward, an integrative approach combining metabolic reprogramming, immunomodulation, and targeted inhibition of CSC vulnerabilities is essential for developing effective CSC-directed therapies. This review discusses the latest advancements in CSC biology, highlights key challenges, and explores future perspectives on translating these findings into clinical applications.
- First author: Haksoo Lee1,2, Byeongsoo Kim1, Junhyeong Park1
- Corresponding author: BuHyun Youn1,3,4
1. Department of Integrated Biological Science, Pusan National University
2. Institute for Future Earth, Pusan National University
3. Department of Biological Sciences, Pusan National University
4. Nuclear Science Research Institute, Pusan National University
- Title of original paper: Cancer stem cells: landscape, challenges and emerging therapeutic innovations
- Journal: Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy
- Web link: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41392-025-02360-2
- Contact e-mail: bhyoun72@pusan.ac.kr
